Comparative Analysis of Obesity-Related Cardiometabolic and Renal Biomarkers in Human Plasma and Serum
Meenu Rohini Rajan, Matus Sotak, Fredrik Barrenäs, Tong Shen, Kamil Borkowski, Nicholas J Ashton, Christina Biörserud, Tomas L Lindahl, Sofia Ramström, Michael Schöll, Per Lindahl, Oliver Fiehn, John W Newman, Rosie Perkins, Ville Wallenius, Stephan Lange, Emma Börgeson Weblink
|
Abstract
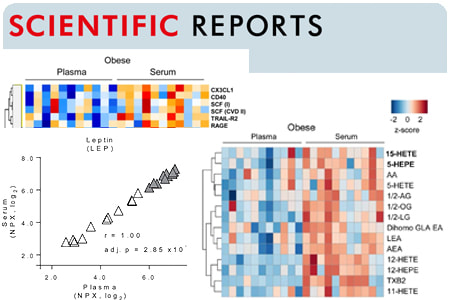
The search for biomarkers associated with obesity-related diseases is ongoing, but it is not clear whether plasma and serum can be used interchangeably in this process. Here we used high-throughput screening to analyze 358 proteins and 76 lipids, selected because of their relevance to obesity-associated diseases, in plasma and serum from age- and sex-matched lean and obese humans. Most of the proteins/lipids had similar concentrations in plasma and serum, but a subset showed significant differences. Notably, a key marker of cardiovascular disease PAI-1 showed a difference in concentration between the obese and lean groups only in plasma. Furthermore, some biomarkers showed poor correlations between plasma and serum, including PCSK9, an important regulator of cholesterol homeostasis. Collectively, our results show that the choice of biofluid may impact study outcome when screening for obesity-related biomarkers and we identify several markers where this will be the case. |
Lipoxin A4 Attenuates Obesity-Induced Adipose Inflammation and Associated Liver and Kidney Disease.
Börgeson E, Johnson AM, Lee YS, Till A, Syed GH, Ali-Shah ST, Guiry PJ, Dalli J, Colas RA, Serhan CN, Sharma K, Godson C.
Cell Metabolism, 2015 Jul 7;22(1):125-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.05.003. Weblink
Cell Metabolism, 2015 Jul 7;22(1):125-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.05.003. Weblink
|
Abstract:
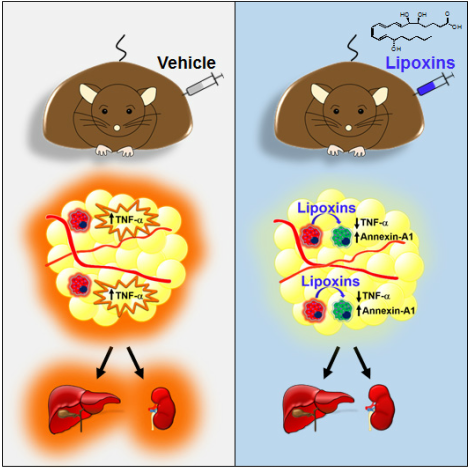
The role of inflammation in obesity-related pathologies is well established. We investigated the therapeutic potential of LipoxinA4 (LXA4:5(S),6(R),15(S)-trihydroxy-7E,9E,11Z,13E,-eicosatetraenoic acid) and a synthetic 15(R)-Benzo-LXA4-analog as interventions in a 3-month high-fat diet (HFD; 60% fat)-induced obesity model. Obesity caused distinct pathologies, including impaired glucose tolerance, adipose inflammation, fatty liver, and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Lipoxins (LXs) attenuated obesity-induced CKD, reducing glomerular expansion, mesangial matrix, and urinary H2O2. Furthermore, LXA4 reduced liver weight, serum alanine-aminotransferase, and hepatic triglycerides. LXA4 decreased obesity-induced adipose inflammation, attenuating TNF-α and CD11c(+) M1-macrophages (MΦs), while restoring CD206(+) M2-MΦs and increasing Annexin-A1. LXs did not affect renal or hepatic MΦs, suggesting protection occurred via attenuation of adipose inflammation. LXs restored adipose expression of autophagy markers LC3-II and p62. LX-mediated protection was demonstrable in adiponectin(-/-) mice, suggesting that the mechanism was adiponectin independent. In conclusion, LXs protect against obesity-induced systemic disease, and these data support a novel therapeutic paradigm for treating obesity and associated pathologies. |
Lipoxin A4 attenuates adipose inflammation.
Börgeson E, McGillicuddy FC, Harford KA, Corrigan N, Higgins DF, Maderna P, Roche HM, Godson C
FASEB Journal. 2012 Oct;26(10):4287-94. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-208249. Weblink
FASEB Journal. 2012 Oct;26(10):4287-94. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-208249. Weblink
Abstract:
Aging and adiposity are associated with chronic low-grade inflammation, which underlies the development of obesity-associated complications, including type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The mechanisms underlying adipose inflammation may include macrophage infiltration and activation, which, in turn, affect insulin sensitivity of adipocytes. There is a growing appreciation that specific lipid mediators (including lipoxins, resolvins, and protectins) can promote the resolution of inflammation. Here, we investigated the effect of lipoxin A4 (LXA4), the predominant endogenously generated lipoxin, on adipose tissue inflammation. Using adipose tissue explants from perigonadal depots of aging female C57BL/6J mice (Animalia, Chordata, Mus musculus) as a model of age-associated adipose inflammation, we report that LXA4 (1 nM) attenuates adipose inflammation, decreasing IL-6 and increasing IL-10 expression (P<0.05). The altered cytokine milieu correlated with increased GLUT-4 and IRS-1 expression, suggesting improved insulin sensitivity. Further investigations revealed the ability of LXA4 to rescue macrophage-induced desensitization to insulin-stimulated signaling and glucose uptake in cultured adipocytes, using vehicle-stimulated cells as controls. This was associated with preservation of Akt activation and reduced secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α. We therefore propose that LXA4 may represent a potentially useful and novel therapeutic strategy to subvert adipose inflammation and insulin resistance, key components of T2DM.
Aging and adiposity are associated with chronic low-grade inflammation, which underlies the development of obesity-associated complications, including type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The mechanisms underlying adipose inflammation may include macrophage infiltration and activation, which, in turn, affect insulin sensitivity of adipocytes. There is a growing appreciation that specific lipid mediators (including lipoxins, resolvins, and protectins) can promote the resolution of inflammation. Here, we investigated the effect of lipoxin A4 (LXA4), the predominant endogenously generated lipoxin, on adipose tissue inflammation. Using adipose tissue explants from perigonadal depots of aging female C57BL/6J mice (Animalia, Chordata, Mus musculus) as a model of age-associated adipose inflammation, we report that LXA4 (1 nM) attenuates adipose inflammation, decreasing IL-6 and increasing IL-10 expression (P<0.05). The altered cytokine milieu correlated with increased GLUT-4 and IRS-1 expression, suggesting improved insulin sensitivity. Further investigations revealed the ability of LXA4 to rescue macrophage-induced desensitization to insulin-stimulated signaling and glucose uptake in cultured adipocytes, using vehicle-stimulated cells as controls. This was associated with preservation of Akt activation and reduced secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α. We therefore propose that LXA4 may represent a potentially useful and novel therapeutic strategy to subvert adipose inflammation and insulin resistance, key components of T2DM.
Lipoxin A₄ inhibits porphyromonas gingivalis-induced aggregation and reactive oxygen species production by modulating neutrophil-platelet interaction and CD11b expression
Börgeson E, Lönn J, Bergström I, Brodin VP, Ramström S, Nayeri F, Särndahl E, Bengtsson T.
Infection and Immunity. 2011 Apr;79(4):1489-97. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00777-10. Web Link.
Infection and Immunity. 2011 Apr;79(4):1489-97. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00777-10. Web Link.
|
Abstract:
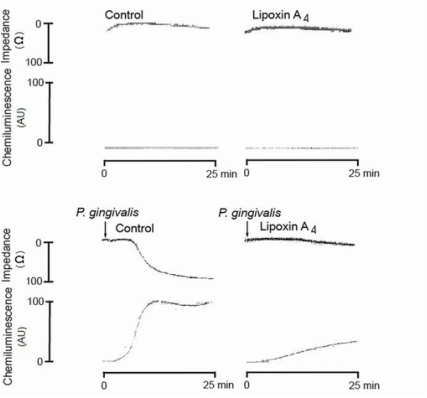
Porphyromonas gingivalis is an etiological agent that is strongly associated with periodontal disease, and it correlates with numerous inflammatory disorders, such as cardiovascular disease. Circulating bacteria may contribute to atherogenesis by promoting CD11b/CD18-mediated interactions between neutrophils and platelets, causing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and aggregation. Lipoxin A₄ (LXA₄) is an endogenous anti-inflammatory and proresolving mediator that is protective of inflammatory disorders. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of LXA₄ on the P. gingivalis-induced activation of neutrophils and platelets and the possible involvement of Rho GTPases and CD11b/CD18 integrins. Platelet/leukocyte aggregation and ROS production was examined by lumiaggregometry and fluorescence microscopy. Integrin activity was studied by flow cytometry, detecting the surface expression of CD11b/CD18 as well as the exposure of the high-affinity integrin epitope, whereas the activation of Rac2/Cdc42 was examined using a glutathione S-transferase pulldown assay. The study shows that P. gingivalis activates Rac2 and Cdc42 and upregulates CD11b/CD18 and its high-affinity epitope on neutrophils, and that these effects are diminished by LXA₄. Furthermore, we found that LXA₄ significantly inhibits P. gingivalis-induced aggregation and ROS generation in whole blood. However, in platelet-depleted blood and in isolated neutrophils and platelets, LXA₄ was unable to inhibit either aggregation or ROS production, respectively. In conclusion, this study suggests that LXA₄ antagonizes P. gingivalis-induced cell activation in a manner that is dependent on leukocyte-platelet interaction, likely via the inhibition of Rho GTPase signaling and the downregulation of CD11b/CD18. These findings may contribute to new strategies in the prevention and treatment of periodontitis-induced inflammatory disorders, e.g. atherosclerosis. |